Tooth Pain and Receding Gums
|
Miguel de Cervantes |
People have two sets of teeth in their lives; the primary teeth are also called the baby, or milk teeth. The minerals found in human teeth and bones that give them their hardness and strength belong to a mineral family known as biological apatites. The apatites found in tooth enamel and dentin. The biological apatites are forms of calcium hydroxyapatite.
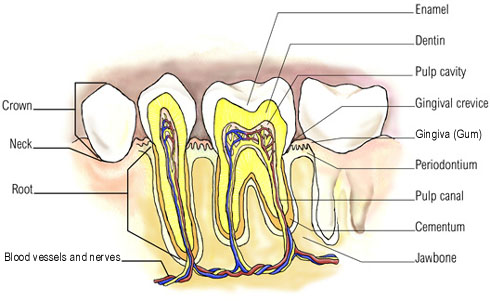
Cementum - a layer of tough, yellowish, bone-like tissue that covers the root of a tooth. It helps hold the tooth in the socket. Cementum, a yellowish substance covering the root of a tooth, is even softer than the enamel and the dentin. Hydroxypatite is its main mineral, comprising about 45 percent of it. Proteins, mainly collagen (the most abundant protein in humans), make up 33 percent of the cementum, while water is left with the remaining 22 percent. The role of the cementum is to help anchor the tooth to the jawbone and ensure its stability.
Crown - the visible part of a tooth.
Dentin - the intermediate tooth layer, the dentin, is harder than bone. Dentin, a yellow-hued substance, makes up most of the tooth. It is responsible for giving the tooth its color. Dentin, which is less mineralized and less brittle than enamel - with 70 percent minerals (hydroxylapatite and calcium phosphate), 20 percent organic materials (primarily proteins) and 10 percent water -acts as a support for enamel. Because dentin is softer, it is more prone to decay.
Enamel - the hard shiny, white outer surface of the tooth is hydroxyapatite, which is a crystalline calcium phosphate. Enamel - the whitish covering - is the hardest and most mineralized part of the teeth and of the entire body. About 96 percent of enamel consists of a mineral called hydroxylapatite, a form of which also makes up to 50 percent of bone. The other 4 percent is water and organic material. Because of its high concentration of mineral power, enamel is strong enough to withstand the stress of biting, chewing and grinding. However, that same trait makes enamel brittle and susceptible to cracking and chipping. Tooth enamel can undergo a process called demineralization if the pH of the mouth falls to lower than normal levels. It happens as combination of nutrition deficiency and mouth bacteria that generates lactic acid. The acidic conditions over time cause the enamel to slowly dissolve, creating tooth cavities.
Nerves and Pulp - nerves transmit signals (conveying messages like hot, cold, or pain) between the brain and the soft center of the tooth. The pulp contains blood vessels and nerves; it nourishes the dentin. As the "nerve" of the tooth, the pulp's major role is to form dentin through biological cells at its outer surface called odontoblasts. The pulp is composed of blood vessels and nerves. Among the cells that make up the pulp are white blood cells like macrophages and T lymphocytes.
Periodontal membrane/ligament - the fleshy tissue between tooth and the tooth socket; it holds the tooth in place.
Root is the anchor of a tooth that extends into the jawbone. The number of roots ranges from one to four.
Dental Pellicle - This is the skin of the tooth. It can reduce dental erosion. The pellicle is damaged or removed by tooth cleaning, but it is supposed to reform quickly.

Teeth are essentially made of calcium and phosphate. There is a constant "traffic" going on in our mouth, with calcium and phosphate migrating in and out of our teeth on a daily basis in response to factors such as chewing hard substances, eating acidic food, and pH and mineral & trace element content of our saliva as well as blood. Saliva and blood composition in turn depend on the quality and mineral content of the food we ingest, our emotional state, any medications we might take, and as far as saliva is concerned, the bacteria population "inhabiting" our mouth and frequently teeth.
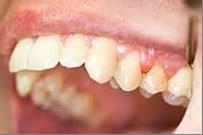
Receding gums is a problem or disease of collagen. Collagen is a tough protein found in bone, skin, cartilage, joints, etc. Diseases of collagen include lupus and other forms of hardening of tissues. On a less significant scale, receding gums represents a failure or dysfunction of the collagen protein between the teeth and gums. The main factors involved in the failure of collagen and receding gums are infection, lack of nutrients including enzymes, diffusible calcium, antioxidants, vitamin C, phosphatase, protein, etc., and poor dental hygiene. The solution is to use both relevant treatments as well as internal treatments to change the root cause of loss of minerals from your teeth. Sometimes the pain can also actually be gum pain, from gum disease or from other gum problems; just be aware of this.
- Causes of teeth and gums problems
- Why teeth and gums should be nourished from inside and outside to be healthy
- How to exercise your teeth and gums
- What it should be done for teeth and gums health
- Home remedies suggestions for tooth pain
- Home remedies suggestions for gum infection